USB and Thunderbolt Standards
 Thunderbolt is an interface technology protocol designed for high-speed transfer of all types of data along a single cable. Thunderbolt cables do not have their own connector designs, relying instead on existing types in the market.
Thunderbolt is an interface technology protocol designed for high-speed transfer of all types of data along a single cable. Thunderbolt cables do not have their own connector designs, relying instead on existing types in the market.
Look for the Thunderbolt icon on a cable or device port to indicate its use of Thunderbolt technology.
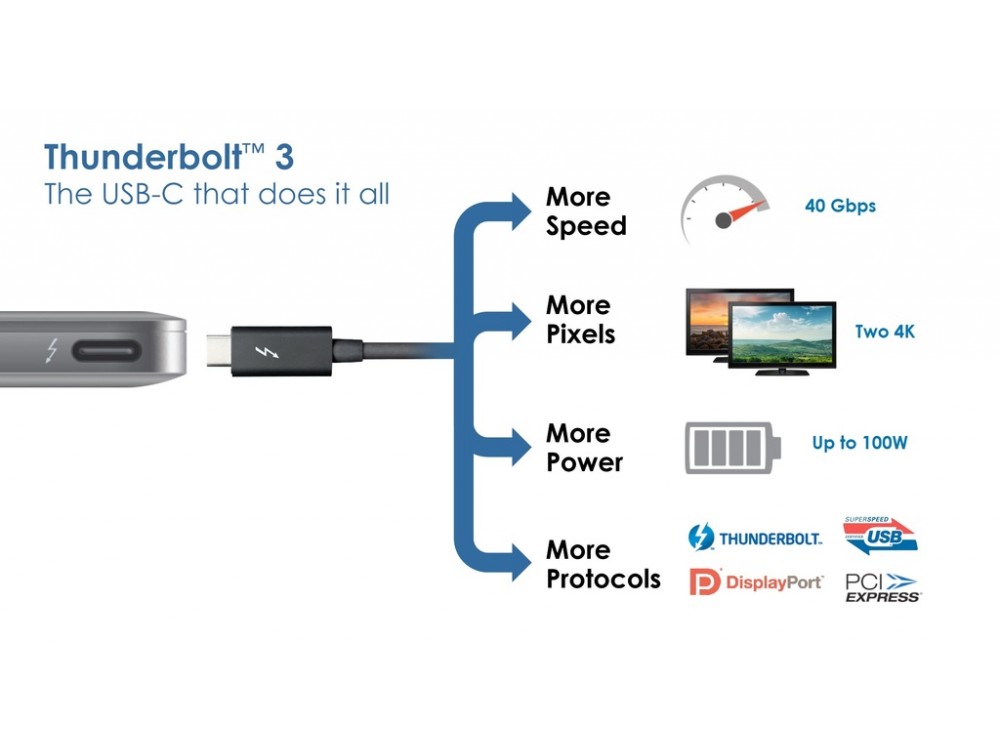
Like USB, Thunderbolt technology comes in different standards that have their own performance ratings and work with different types of connection hardware. This includes Thunderbolt 1, Thunderbolt 2, which works with Mini DisplayPort connectors, and the newest Thunderbolt 3, which works with USB-C connectors.
Not all USB-C connections use Thunderbolt technology (as shown in below Table), but those that support Thunderbolt 3 can provide unprecedented speed and power delivery.
Let's take a closer look at the elements distinguishing USB and Thunderbolt standards. Simply put, these are speed, connector types and added functionality.
| Standard | Also Known as | Logo | Year Introduced | Connector Types | Max Data Rate |
| USB 1.1 | Full-Speed USB | 1998 | USB-A USB-B | 12 Mbps | |
| USB 2.0 | High-Speed USB |
| 2000 | USB-A USB-B USB Micro A USB Micro B USB Mini A USB Mini B | 480 Mbps |
| USB 3.0 | USB 3.1 GEN 1 SuperSpeed USB |
| 2008 | USB-A | 5 Gbps |
| USB 3.1 | USB 3.1 GEN 2 SuperSpeed+ SuperSpeed USB 10Gbps |
| 2013 | USB-A | 10 Gbps |
| USB 3.2 | SuperSpeed USB 20Gbps |
| 2017 | USB-C | 20 Gbps |
| Thunderbolt 1 |
| 2011 | Mini DisplayPort | 10 Gbps | |
| Thunderbolt 2 |
| 2013 | Mini DisplayPort | 20 Gbps | |
| Thunderbolt 3 |
| 2015 | USB-C | 40 Gbps | |
| USB 4 |
| 2019 | USB-C | 40 Gbps | |
| Thanderbolt 4 | 2020 | USB-C | 40Gbps |




Leave your comment